Winter Storm Uri: What, Who, How and Why Texas’ Power Grid and ERCOT Failed Houston
An Overview of the Texas Power Market to Understand the Impacts of Winter Storm Uri
Written by Michelle Avalos, Deputy Director of Impact Hub Houston
It’s February 22, 2021, and millions are dealing with the aftermath of the winter storm that ran across Texas last week. As our community bands together, mourns the friends and family we’ve lost, and aid begins to reach Houstonians in need, some of us are starting to piece together the facts so we may be able to co-create recovery and resiliency solutions to prevent this from ever happening again.
To support these efforts, we’ve put together a high level and unbiased outline focusing on mapping the existing process and infrastructure of the Texas power market. We hope this will give you some clarity and allow you to better problem solve as we move forward.
The first thing you need to know is that the United States is broken up into three primary power market transmission grids called the Western, Eastern and Texas Interconnection. Yup, most of Texas stands alone. Why? Interestingly enough, our grid underwent changes in 1970 after a major blackout that occurred in the Northeast in 1965. Since then, our state’s power grid has undergone several hiccups, but we’ve continued to remain independent from the rest of the country, with only minor connections to the Eastern and Western grids as well as to Northern Mexico’s grid. If you want to dig deeper into the history, check out this article by the Chron.
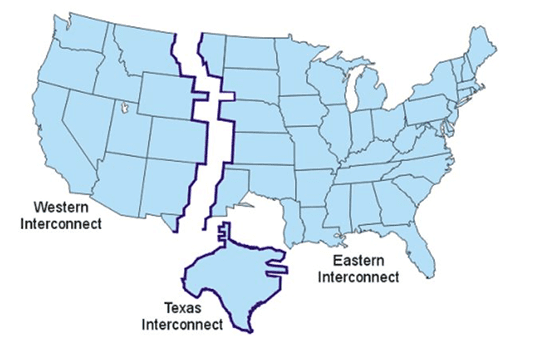
Figure 1. U.S. Power Grid Map (Source: EPA)
There are two primary characteristics of the Texas Interconnect:
- The Texas grid system has minimal transmission interconnections to the other grids in the U.S.; and,
- Our power market is largely unregulated, which means no single entity has a monopoly on the sale of electricity in the state. As a result, across most of Texas, consumers can choose their electricity provider.
Our power market is run by a power grid operator, or Independent System Operator (ISO), called The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, or “ERCOT.” There are six other ISOs in the U.S. and a couple more in Canada. (See Figure 2.)
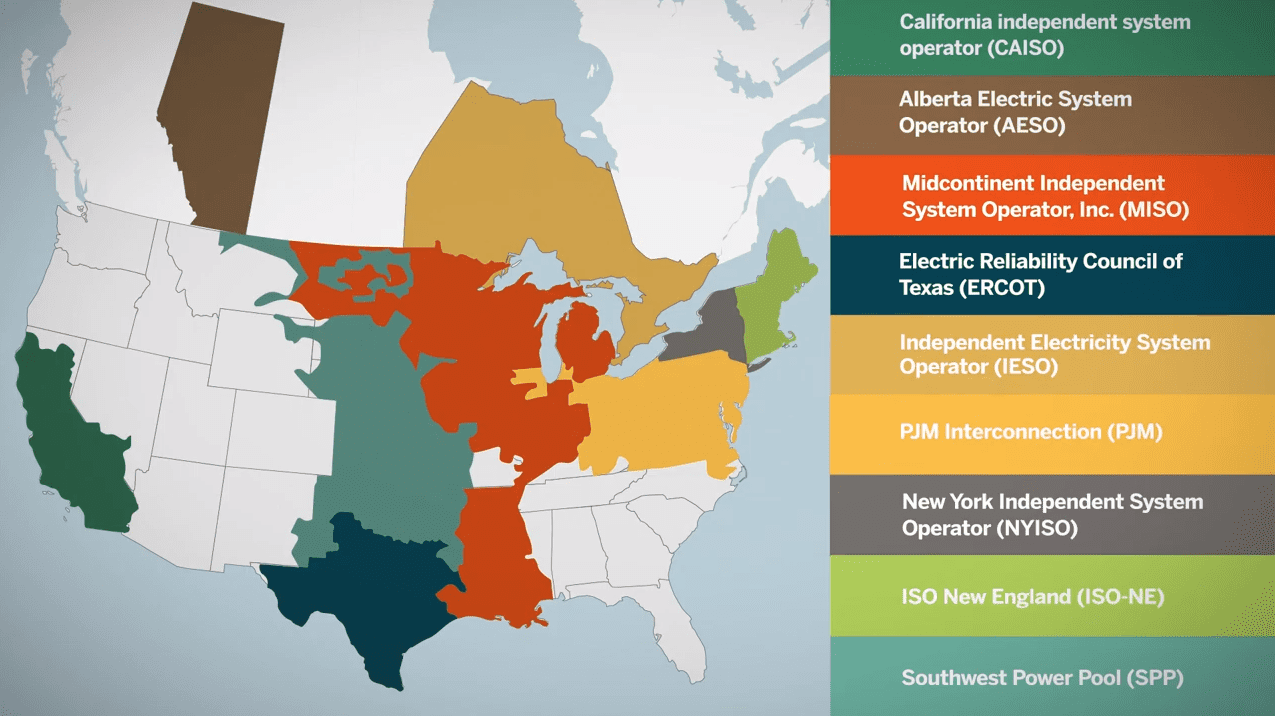
Figure 2. Map of Other ISOs in North America (Source: CME Group)
ERCOT, however, is one of the least interconnected to the rest of the country’s grid. In a way, you can say that ERCOT is an island, which you can see more clearly in Figure 3, below.
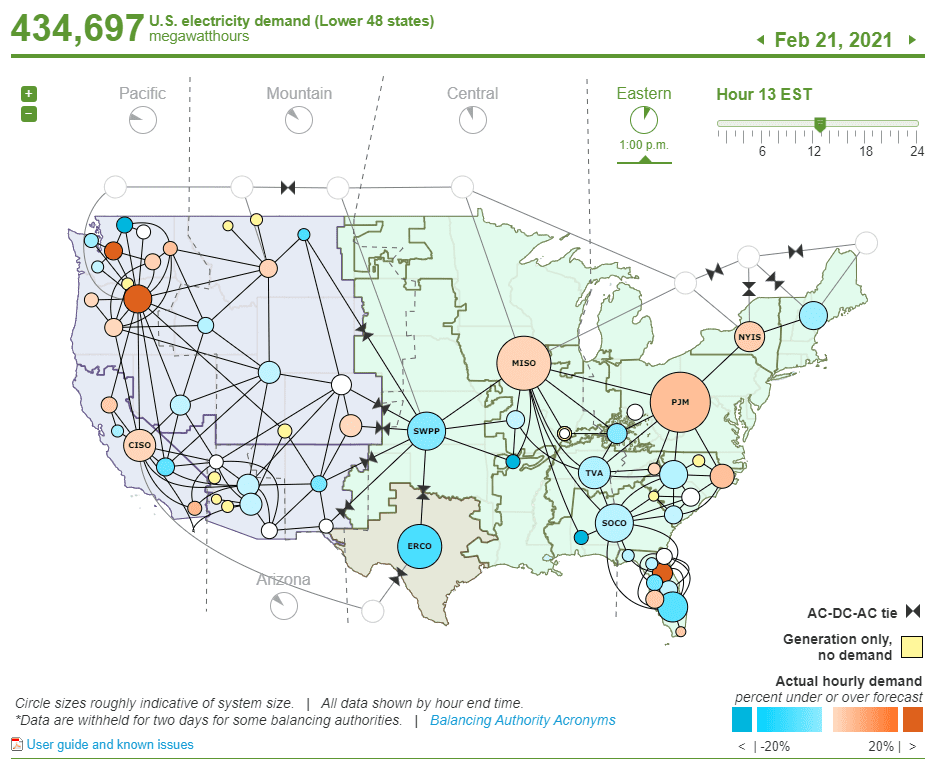
Figure 3. Map of U.S. Grid Interconnections (Source: EIA)
So, what is behind our “Power to Choose” in Texas?
A lot of people assume that their electricity provider is also the one generating the actual power for their homes or businesses. Nope. In fact, for most providers, this is not the case.
While some electricity providers own generation facilities, most are just retailers who purchase power in bulk from the wholesale market, then, mark up the price to sell it to customers on the retail market. In other words, most of the electricity providers we have accounts with are like grocery stores: They are responsible for selling, managing, and providing support to the customers (you and me), while profiting from their retail price markup margins. In the Houston area, there are about 50 of these companies for the residential sector.
Some people think that CenterPoint Energy is the one generating our power in Houston. Not true. CenterPoint Energy is responsible for the delivery of power and maintains the infrastructure (wires/ poles) that allows electricity to reach the 2.3 million customers in the Houston metro area. CenterPoint Energy also distributes natural gas for cooking and heating, but they do *not* generate or sell electricity to customers.
So then, who actually produces our electricity?
There are 500+ independent power generators across Texas. They own and operate the power plants that convert various fuels and renewables into electricity for our power grid. However, the power generators across our state do not decide when and how much power is produced for customers. They are only able to submit offers to sell their generation capacity at a given price in hopes that they will be selected (or dispatched) to supply electricity to meet the markets demand for energy. These offers get sorted into a “supply stack” and dispatched daily starting with the lowest price offers.
Who tracks our power needs and signals the power generators to produce electricity?
ERCOT, our power grid operator, is responsible for properly managing the supply of power to meet the actual or “real-time” demand and importantly, the system operator must ensure a balanced market at all times. What balancing really means is that if power demand is greater than the available power supply, ERCOT will forcibly reduce demand by executing power blackouts. ERCOT estimates short and long term power needs, but ultimately, the market supply and demand balance is managed by 24/7 operations. The forecast generated by ERCOT serves to let power generations know when they might be needed but does not give them any guarantee that they will be dispatched.
Is ERCOT the one buying and selling the electricity for the grid?
No. ERCOT does not buy or sell the electricity on our power grid. They just coordinate the various pieces to ensure balance. You can think of ERCOT as a real time matchmaker between the power generators and our demand for electricity. The buying and selling ultimately happens 1) on the wholesale market (between the power generators and the electricity providers) and 2) on the retail market (between the electricity retailers/providers and the commercial/residential customers).
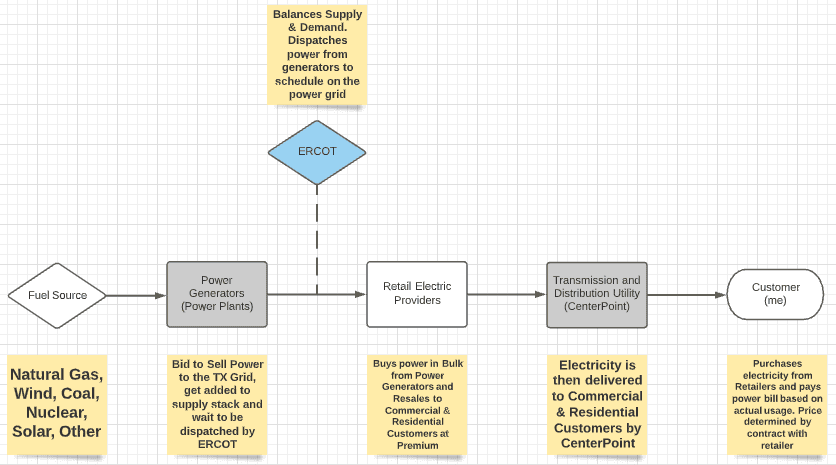
Figure 4. Flow of Electricity under ERCOT Structure
Before we move to outline the impacts of the winter storm, here are a couple more important factors you need to know about our power market:
We explained how the deregulated market works for you as the customer, but how does the market impact the companies who are producing our electricity?
The power generators that operate inside of ERCOT make decisions about their fuel source, infrastructure, operating schedule and more based on forecasted demand trends and their need to operate a profitable business. These power generators only make money when ERCOT selects their price offer for a certain amount of electricity and dispatches their power plant to add electricity supply to the grid. The power generators receive revenues only for the actual amount of electricity that is dispatched by ERCOT and consumed by the end user. If you are a power generator and your price offer is not selected by ERCOT, you don’t make money that day and your power plant just sits there. This revenue structure is referred to as an energy payment.
In Texas, most power generators receive the bulk of their energy payments in the peak summer months, particularly late July and August. During the winter months, when our state’s electricity demand is typically lower, some power generators tend to schedule power plant maintenance or full shutdowns because the likelihood that they will be dispatched and paid to generate power is significantly lower.
Seems pretty straight forward, right?
Well, this is how the structure defers from other states:
Power generators that operate in a regulated market also get paid a capacity payment which is calculated based on the maximum output that the power generator can produce. States that offer capacity payments to power generators will pay the amount even if the respective power plant is not called upon to produce electricity. Essentially, the state pays the capacity payment to have the power plants built and available as needed. When those plants are dispatched, energy payments will also kick in.
Power generators operating inside of ERCOT do not receive capacity payments: They do NOT get paid to be on standby. This payment structure lowers the power generator’s incentive to make other significant investments to their facilities.
So, how did Winter Storm Uri shock the ERCOT power grid?
There are a fair share of articles to choose from that are aiming to answer this question. Here’s a brief summary:
- The Texas grid is set up to support peak demand during the summer heat but doesn’t have similar reliability measures in place during our winter months.
- Last week, electricity demand for heating spiked as a response to the winter storm.
- The spike in demand occurred in the midst of scheduled power plant maintenance and shutdowns which traditionally take place during winter in Texas. These are referred to as planned plant outages.
- The power plants that were actually operating and able to generate electricity for us also ran into unplanned outages caused by the extreme weather conditions.
- This combination further cut the supply of electricity to the grid.
- ERCOT’s supply stack became very thin and it was not able to dispatch sufficient power generators to meet our electricity needs.
- Millions were left without power for days.
- While the power generators worked to get their facilities back online and ERCOT worked to prevent a full system shutdown, pressure was placed on the consumer (you and me) to conserve power.
- After a series of rotating outages and forced power cuts, more Houstonians began to regain power until eventually, ERCOT’s supply stack was replenished and supply and demand was rebalanced. This was also supported by a drop in heating demand from the customers once the extreme weather had past.
Our largest bottlenecks during the storm were both the physical infrastructure and the nature of how our power grid functions.
As mentioned , February is historically not a peak demand season in Texas. This meant that several power plants were previously scheduled to undergo maintenance because they didn’t expect to be called upon to generate power this month. The maintenance process varies by power plant type, age and other factors. The duration of the maintenance can last for days, weeks or months depending on the needs of the respective power plant. Once a power plant is undergoing maintenance or a full shutdown, they can’t immediately flip the switch to be back online.
On February 8, ERCOT sent an Operating Conditions Notice (OCN) to all power generators to prepare their power plants for the anticipated winter storm. The Chron outlines the timeline that followed in this article which is derived from the Operating Messages sent by ERCOT in the days to follow.
Power generators received about a four to five day notice to prepare their facilities. Whether or not this was sufficient time for the power plants that were offline to come back online is truly dependent on where they were in their maintenance/shutdown process.
As the winter storm moved in, we also began to see unplanned outages at the power plants that were still online. These outages occurred for a couple of reasons: 1) infrastructure at the facilities was not prepared for harsh winter weather, and 2) at some point, access to the fuel sources was also obstructed by the winter weather conditions.
Why didn’t we have any back up power?
Looping back to how our power generator makes money: Since they only receive “energy payments” and not “capacity payments,” power generators are not incentivized to build and manage back up power facilities, so they don’t.
In a time of crisis, our “Power to Choose” worked against us.
The outcomes of Winter Storm Uri shed a light on fundamental opportunities for improvement to our power grid. The same structure that was set up to save us money on electricity, also worked to disincentives investments in infrastructure that could have prevented the massive outages that occurred last week.
There are so many other factors we can discuss around this topic, but for now, we want to leave you with an objective outline so that you, dear problem solver, can use this information as you digest and prepare for the decisions to come.
What will Texas choose going forward?
What do we truly want as consumers when it comes to our access to electricity?
—
Helpful Links for Additional Research:
- ERCOT Urgent Board of Directors Meeting on Feb 24 🡪 http://www.ercot.com/calendar/2021/2/24/225372-BOARD
- ERCOT Fact Sheet Feb. 2021 🡪 http://www.ercot.com/content/wcm/lists/219736/ERCOT_Fact_Sheet_2.12.21.pdf
- Deep dive into ERCOT Operating Procedures 🡪 http://www.ercot.com/mktrules/guides/procedures
- Dive into ERCOT Operations Messages leading up to the winter storm 🡪 http://www.ercot.com/services/comm/mkt_notices/opsmessages
- Directory of Power Generators in Texas 🡪 https://www.puc.texas.gov/industry/electric/directories/pgc/alpha_pgc.aspx
- Learn about ERCOT Membership and view the full list of members 🡪 http://www.ercot.com/about/governance/members/
- Article: “Why does Texas have its own power grid?” 🡪 https://www.chron.com/news/houston-texas/article/Why-does-Texas-have-its-own-power-grid-15958412.php
- History of Electric Deregulation in Texas 🡪 http://tcaptx.com/downloads/HISTORY-OF-DEREGULATION.pdf
- Understanding Basics of the Power Market Video by CME Group 🡪 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dYvEG3uQzsQ
